Ebola: The reality of an interconnected world
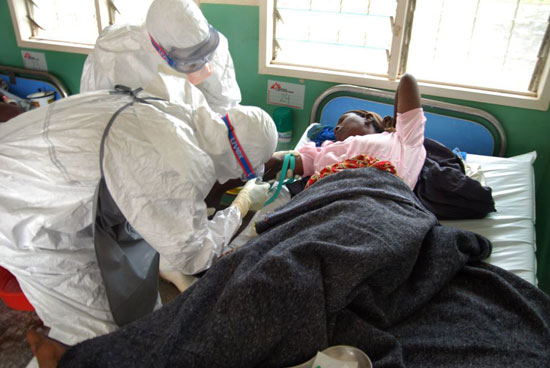
Advances in aviation technology and the industry and globalisation have made the world to become a very inter-connected space with obvious opportunities and challenges. An individual may contract an infection from one part of the world and can spread it to a very distant land in a matter of days while incubating the pathogen without discernible symptoms.
WHILE I was writing this piece, I received a news alert from Washington Post, about the arrival to the United States of Dr Kent Brantly, an American doctor, who was infected with the Ebola virus disease while working in Liberia with a Christian missionary organisation – Samaritan Purse.
His repatriation to his country was not without controversy. In recent times, there are perhaps fewer diseases that have been more polarising of the US public opinion as Ebola.
The virus, although lethal, has a reproduction number – the average number of secondary cases arising from one infectious case in a totally susceptible population – of one compared to say measles, greater than 12.
When his repatriation to Emory University Teaching Hospital, Atlanta, was mooted, some talking heads went into overdrive. Some were very indignant and vociferous about the repatriation. An equally significant number came down on the side of the repatriation.
The recent decision by the Nigerian government to suspend the Asky flights from operating in the country, while it investigates sequences and events surrounding the air travel of the deceased is a commendable public health measure.
However, it is uncertain if Nigeria has a robust coherent strategy to deal with an outbreak of Ebola, if one goes by its predilection for being mired in the muck of indecision on matters of public concerns and national security.
Further, Ebola couldn’t have chosen a more salubrious period to visit Nigeria; particularly at a time when its doctors – in public sector – have remained on strike with no end in sight; decades of poor investment in healthcare and medical research; derelict and dilapidated healthcare infrastructure, poor regulatory measures and derisory budgetary allocation and poor capability within the sector.
A country where attempts at healthcare reform have remained a Sisyphean task will only accentuate the virulence and epidemic reach of Ebola.
In parallel to these challenges are externalities such as poor education, lack of access to healthcare facilities, illiteracy and superstitions and suspicion of healthcare facilities; insecurity and instability in large swathes of its population, particularly in northern Nigeria and its un-policed porous borders.
An Interconnected World
Most countries and their leadership are worried by the current outbreak of Ebola; in spite of the fact that these countries may be distant from where the theatre of infection is wreaking the havoc. Further, Ebola is a delicate, very slowly mutating filovirus with a very low reproduction number; and it is not as contagious as bird flu and Middle East respiratory virus (MERS) that has been reported in the US. Given its delicate nature, washing with soap and water — outside its host – renders it less contagious. Besides, evidence suggests that asymptomatic individuals are mostly non-contagious.
In spite of these, the current panic mainly in the developed world may unfortunately inform decisions and policies in response to the outbreak by their government – which may have practical implications on the sub-Saharan countries grappling with the blighting battle with Ebola. It can be argued that such response may be understandable – irrespective of the facts.
The recent outbreak has caused more fatalities than any previous outbreaks – since it was first reported in two simultaneous outbreaks in 1976 in Nzara, Sudan and in Yambuku, Zaire (now Democratic Republic of Congo).
The latter was in a village close to Ebola River -where the name was derived. Further, the current strain – Zaire-strain -is more virulent than other strains. Besides, previous outbreaks have been confined to villages and rural Africa.
Further, with the virus, one can’t have a good death, given that most infected patients die isolated painful death – physically and psychologically separated from their families and loved ones.
Beyond factors intrinsically linked to the virus, are some externalities.
Most countries, particularly Western nations are concerned about the lack of coherent strategic response by the governments in the sub-Saharan Africa where mortality from the virus continues unabated.
Further, their concern and the scare may stem from value judgment and crisis of confidence on the institutional capabilities, capacities, effectiveness and expertise intrinsic to healthcare systems in the affected countries. Decades of neglect, poor regulation and investment and the degradation of their health infrastructure tend to lend some credence to those negative emotion and evaluation.
To drive home the point, it is most concerning to note that the continent of Africa has a mere 3 percent of the global health workforce while at the same time, it accounts for 24 percent of the global burden of disease. This disconnect is most disturbing and requires urgent attention by its leadership and policy makers.
All things considered, it is most unsurprising that in moment of crisis, where confidence in the system is in short supply, heuristic appraisal and perception inform loose guide thinking and responses. Further, the democratisation of travel has made it possible for people to move within and across continents, countries and regions within a matter of a few hours to a couple of days.
Incubation periods of most infectious diseases last longer than these. Suffice it to say that advances in aviation technology and the industry and globalisation have made the world to become a very inter-connected space with obvious opportunities and challenges. An individual may contract an infection from one part of the world and can spread it to a very distant land in a matter of days while incubating the pathogen without discernible symptoms.
Given the foregoing, public health concern or other events with socio-economic and political implications can easily metastasise to places far flung from the origin of such perturbation. Some governments and their policy makers – particularly in the West – notwithstanding the foregoing are loath to view the interconnectedness from the optics of current reality.
Investments in infectious diseases research have nose-dived in most of these countries and funding for infectious diseases clinics has drastically reduced as part of a drive for efficiency savings. The private sector has not fared any better, particularly the pharmaceutical industry that is well known for its Darwinian approach to portfolio management.
For years, it has rechannelled resources and infrastructure for research in infectious diseases to more lucrative pipelines.
In a very strange way, Ebola has reminded us about the fragility of life. Our common humanity and the interconnectedness of our global village should inform our public policy and humanitarian advocacy.
In order to effectively tackle this immediate public health challenge, there should be local co-ordination and co-operation – taking advantage of information and expertise on the ground – and support from the international community.
In the intermediate and long term, there needs to be an enriched space for comprehensive collaboration to help with sharing of information, knowledge and expertise; and creation of institutional capability and capacity that encourage proactive responses.
Anayo Unachukwu is a psychiatrist based in the UK. He has interest in medico-legal issues and the impact of inequality on health. This article is reproduced from The African Executive







Comments